A Journey Through Time: Exploring the History of Jewelry
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the History of Jewelry
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the History of Jewelry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the History of Jewelry

Jewelry, a timeless art form and a testament to human creativity, has adorned individuals for millennia. More than mere adornment, jewelry reflects cultural values, social status, and personal beliefs, weaving a rich tapestry of history across civilizations. This exploration delves into the fascinating evolution of jewelry, tracing its roots from ancient origins to modern innovations.
The Dawn of Adornment: Jewelry in Prehistory
The earliest traces of jewelry can be found in the Paleolithic era, with evidence of personal adornment dating back as far as 100,000 years ago. Early humans used natural materials like shells, bones, and teeth to create simple necklaces, bracelets, and pendants. These rudimentary ornaments served both practical and symbolic purposes. Shells, for instance, could be used for decoration and also for their potential medicinal properties.
The Neolithic era, marked by the rise of agriculture and settled communities, saw a significant advancement in jewelry-making. Tools like grinding stones allowed for the creation of more intricate designs, and the use of materials like polished stone and pottery became prevalent. This period also saw the emergence of specialized artisans who crafted jewelry for both personal and ceremonial use.
Ancient Civilizations: Jewelry as a Symbol of Power and Status
Ancient civilizations across the globe developed distinct jewelry traditions, each reflecting their unique cultural values and beliefs.
-
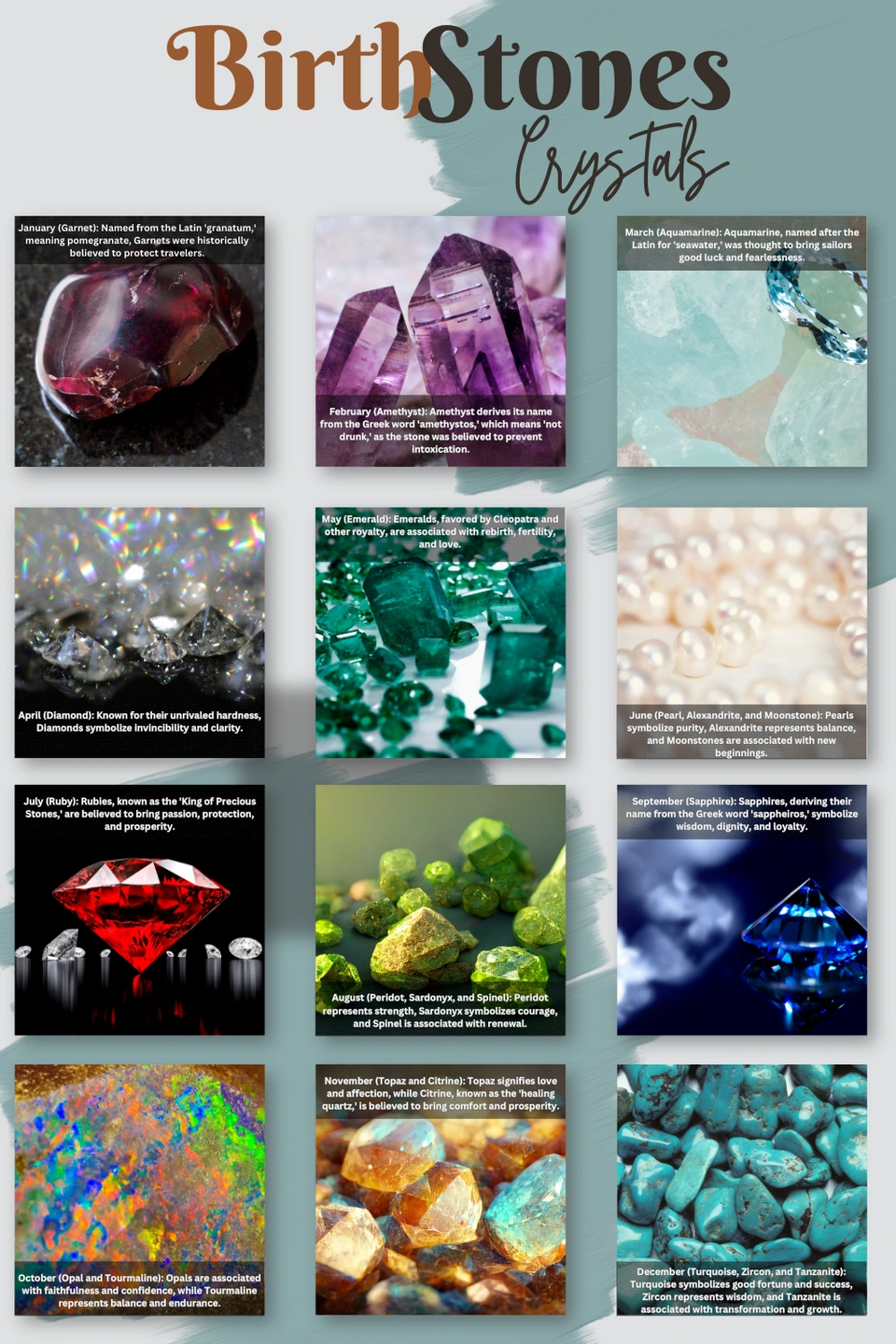
Ancient Egypt: Known for its opulent and elaborate jewelry, ancient Egypt saw gold as a symbol of divinity and immortality. The intricate techniques of goldsmithing and the use of precious stones like lapis lazuli, turquoise, and carnelian resulted in iconic pieces like scarab beetles, amulets, and elaborate collars. These pieces not only adorned the wealthy but also served as powerful symbols of religious and social status.
-
Mesopotamia: Mesopotamian jewelry, characterized by its use of intricate geometric patterns and the incorporation of precious metals and gemstones, was a reflection of the region’s advanced civilization. The use of gold, silver, and bronze, along with semi-precious stones like carnelian and agate, resulted in elaborate necklaces, bracelets, and earrings that showcased both artistry and wealth.
-
Ancient Greece and Rome: Greek and Roman jewelry reflected the classical ideals of beauty and harmony. Gold, silver, and bronze were the primary materials, often adorned with intricate engravings, filigree work, and gemstones like emeralds, sapphires, and pearls. The use of cameos, which featured intricate portraits carved in shell, became a popular form of jewelry during this period.
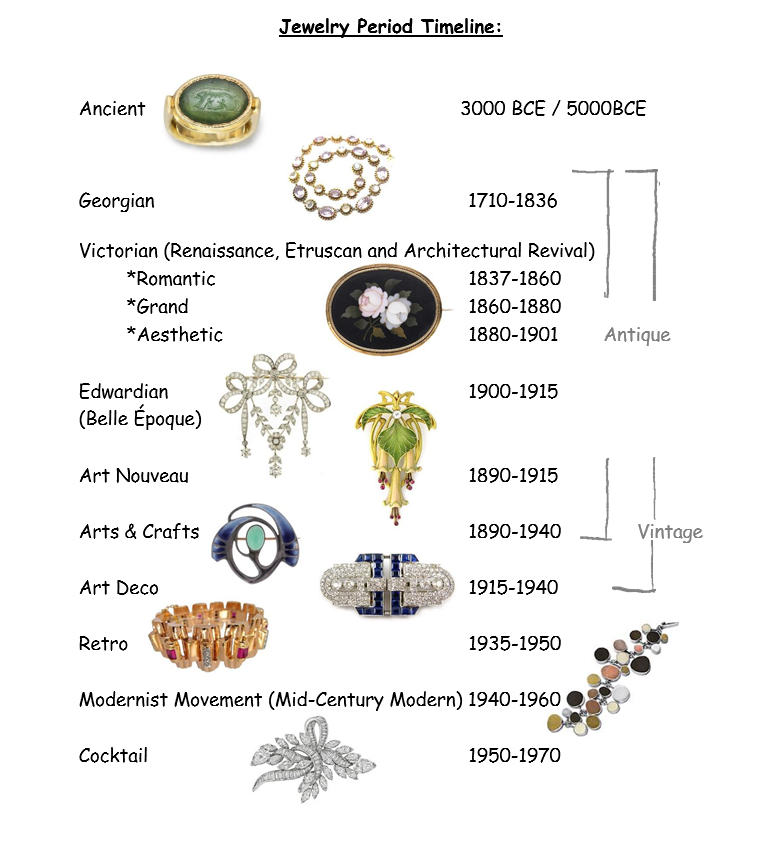
The Middle Ages and Renaissance: Jewelry as a Reflection of Faith and Fashion
The Middle Ages saw a significant shift in jewelry design, influenced by the prevailing religious beliefs of the time. Religious symbols like crosses, Virgin Mary pendants, and devotional images became prominent, reflecting the importance of faith in daily life.
The Renaissance, with its rediscovery of classical art and culture, brought a renewed emphasis on beauty and craftsmanship. Jewelry became more intricate and elaborate, featuring elaborate designs, precious gemstones, and enamel work. The use of pearls, emeralds, and rubies became particularly popular, reflecting the wealth and sophistication of the era.
The 17th and 18th Centuries: Jewelry as a Symbol of Courtly Elegance
The 17th and 18th centuries witnessed a flourishing of jewelry styles, influenced by the grandeur of royal courts. The Baroque period, characterized by its dramatic and ornate designs, saw the use of elaborate floral motifs, asymmetrical shapes, and intricate gemstones. This period also saw the rise of the diamond, which quickly became a symbol of wealth and power.
The Rococo period, with its emphasis on grace and elegance, brought a lighter and more playful style to jewelry. Pearls, delicate floral motifs, and intricate pastel colors became popular, reflecting the era’s emphasis on femininity and refinement.
The 19th Century: Jewelry as a Reflection of Romanticism and Industrialism
The 19th century saw a fusion of romanticism and industrialism in jewelry design. The Romantic movement, with its emphasis on emotion and nature, inspired jewelry featuring floral motifs, sentimental themes, and the use of natural materials like coral and amber.
The Industrial Revolution, meanwhile, led to the development of new techniques and materials, like the use of platinum and the invention of the diamond-cutting machine. These innovations allowed for the creation of more intricate and durable pieces, reflecting the era’s focus on progress and technological advancements.
The 20th Century: Jewelry as a Statement of Modernity and Individuality
The 20th century saw a dramatic shift in jewelry design, reflecting the changing social landscape and the rise of new artistic movements. Art Deco, with its geometric patterns, bold colors, and use of exotic materials like onyx and jade, captured the spirit of modernity and urban life.
The rise of Surrealism in the 1920s and 1930s influenced jewelry design, leading to the creation of pieces that challenged traditional notions of beauty and explored the subconscious mind. These pieces often featured unexpected shapes, textures, and materials, reflecting the era’s fascination with the bizarre and the unconventional.
The mid-20th century saw a resurgence of interest in traditional craftsmanship, with designers like Cartier and Van Cleef & Arpels creating exquisite pieces that blended classic elegance with modern techniques. The latter half of the century saw the rise of minimalist and conceptual jewelry, with designers like Elsa Peretti and David Webb exploring new forms and materials.
The 21st Century: Jewelry as a Fusion of Tradition and Innovation
The 21st century continues to be a dynamic period for jewelry design, with designers drawing inspiration from a wide range of sources, from ancient traditions to cutting-edge technology. The use of new materials, such as titanium, ceramic, and recycled materials, reflects a growing concern for sustainability and environmental responsibility.
Contemporary jewelry also embraces a wide range of styles, from the bold and statement-making to the delicate and minimalist. The rise of online platforms has made it easier for independent designers to showcase their work, leading to a more diverse and eclectic landscape of jewelry design.
The Importance of Jewelry Throughout History
Jewelry has played a significant role in human history, serving a multitude of purposes beyond simple adornment. Its importance can be understood through various facets:
-
Social Status and Identity: Throughout history, jewelry has been a powerful symbol of social status and identity. The use of precious metals and gemstones often indicated wealth and power, while specific types of jewelry could signify membership in a particular social group or profession.
-
Religious and Spiritual Beliefs: Jewelry has played a significant role in religious and spiritual practices across cultures. Amulets and talismans were often worn for protection and good luck, while religious symbols like crosses, stars of David, and crescent moons were used to express faith and devotion.
-
Cultural Expression: Jewelry has served as a powerful means of cultural expression, reflecting the values, beliefs, and aesthetics of different societies. Traditional jewelry styles, from the intricate designs of Indian jewelry to the minimalist aesthetics of Scandinavian jewelry, provide insights into the unique cultural identities of different groups.
-
Personal Expression: Jewelry allows individuals to express their personal style and individuality. From the bold statement pieces worn by fashion icons to the sentimental keepsakes cherished by individuals, jewelry reflects personal tastes, values, and experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions About Jewelry History
1. What are the oldest known examples of jewelry?
The oldest known examples of jewelry date back to the Paleolithic era, around 100,000 years ago. These early pieces were made from natural materials like shells, bones, and teeth.
2. What materials were used in ancient jewelry?
Ancient civilizations used a variety of materials for jewelry, including:
- Precious metals: Gold, silver, bronze
- Gemstones: Lapis lazuli, turquoise, carnelian, emerald, sapphire, pearl
- Natural materials: Shells, bones, teeth, amber, coral
3. What are some of the most iconic jewelry styles throughout history?
Some of the most iconic jewelry styles throughout history include:
- Ancient Egyptian jewelry: Scarab beetles, amulets, elaborate collars
- Mesopotamian jewelry: Intricate geometric patterns, use of precious metals and gemstones
- Greek and Roman jewelry: Cameos, intricate engravings, filigree work
- Medieval jewelry: Religious symbols like crosses and Virgin Mary pendants
- Renaissance jewelry: Elaborate designs, precious gemstones, enamel work
- Baroque jewelry: Dramatic and ornate designs, floral motifs, asymmetrical shapes
- Rococo jewelry: Delicate floral motifs, pastel colors, emphasis on femininity
- Art Deco jewelry: Geometric patterns, bold colors, exotic materials
- Surrealist jewelry: Unexpected shapes, textures, and materials
4. How has technology influenced jewelry design?
Technology has played a significant role in shaping jewelry design throughout history. Innovations like the diamond-cutting machine, the development of new materials like platinum, and the advent of computer-aided design (CAD) have allowed for the creation of more intricate, durable, and innovative pieces.
5. What are some of the trends in contemporary jewelry design?
Contemporary jewelry design is characterized by a fusion of tradition and innovation, with designers drawing inspiration from a wide range of sources. Some of the key trends include:
- Sustainability: The use of recycled materials and ethical sourcing practices
- Minimalism: Clean lines, simple shapes, and a focus on functionality
- Statement pieces: Bold and eye-catching designs that make a statement
- Personalization: Customized pieces that reflect individual style and preferences
- Technology: The use of 3D printing, laser cutting, and other technologies to create innovative designs
Tips for Appreciating and Collecting Jewelry
-
Research and Learn: Familiarize yourself with different jewelry styles, materials, and techniques. Explore books, online resources, and museum exhibits to broaden your knowledge.
-
Consider Your Personal Style: Choose jewelry that reflects your own taste and personality. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different styles and materials.
-
Look for Quality and Craftsmanship: Pay attention to the details of the jewelry, such as the quality of the materials, the craftsmanship, and the design.
-
Invest in Pieces You Love: Jewelry is a timeless investment. Choose pieces that you will cherish for years to come.
-
Take Care of Your Jewelry: Store your jewelry properly to prevent damage and wear. Have pieces cleaned and repaired as needed.
Conclusion
The history of jewelry is a captivating journey through time, reflecting the evolution of human creativity, cultural values, and technological advancements. From the simple adornments of prehistoric humans to the intricate creations of contemporary designers, jewelry has played a multifaceted role in shaping our understanding of beauty, identity, and the human experience. As we continue to explore and appreciate the rich history of jewelry, we gain a deeper appreciation for the enduring power of this timeless art form.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the History of Jewelry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!