Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on Jewelry in India
Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on Jewelry in India
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on Jewelry in India. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on Jewelry in India
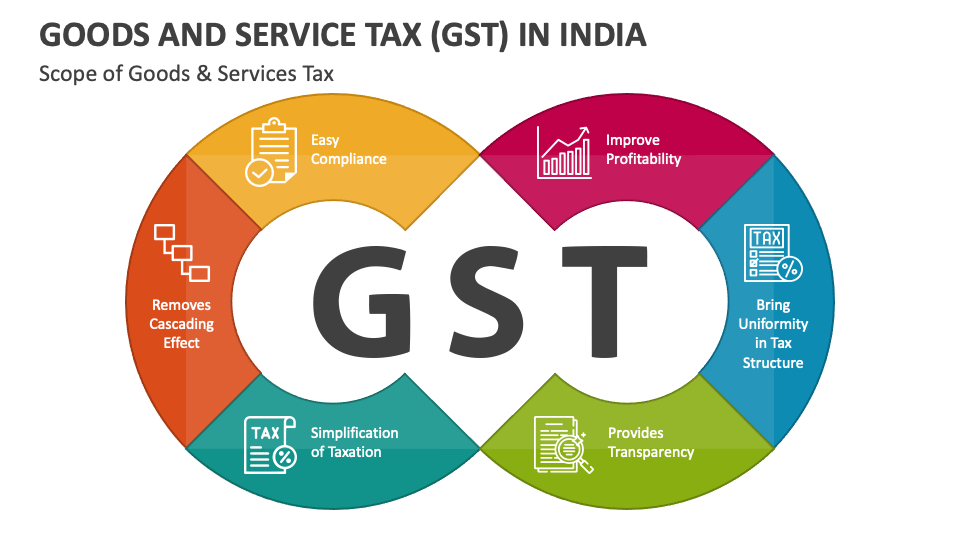
The Indian jewelry industry, a vibrant tapestry of craftsmanship and tradition, operates within a complex regulatory framework. One of the most significant aspects of this framework is the Goods and Services Tax (GST), a nationwide indirect tax that applies to the sale, manufacture, and import of goods and services.
This article aims to demystify the intricacies of GST as it pertains to the jewelry sector in India. We will delve into the specific rates applicable to different types of jewelry, highlight the implications of these rates, and provide a comprehensive understanding of the nuances surrounding GST in the jewelry industry.
The Foundation of GST: A Simplified Overview
GST, introduced in India in 2017, replaced a multitude of indirect taxes, streamlining the taxation system and creating a unified market. The core principle of GST is to levy tax on the value added at each stage of the production and distribution chain, ensuring that the final consumer bears the tax only once.
Understanding the GST Rates for Jewelry
The GST rates for jewelry vary depending on the type of precious metal and gemstone used. These rates are categorized as follows:
1. Gold and Silver Jewelry:
- Gold jewelry is subject to a 3% GST rate (excluding gold coins and bars). This rate applies to all forms of gold jewelry, including ornaments, chains, bangles, earrings, rings, and pendants.
- Silver jewelry also attracts a 3% GST rate, similar to gold jewelry. This includes silver ornaments, chains, bangles, earrings, rings, and pendants.
2. Platinum and Other Precious Metal Jewelry:
- Platinum jewelry is subject to a 3% GST rate, aligning with gold and silver jewelry.
- Jewelry made from other precious metals like palladium, rhodium, and iridium also falls under the 3% GST rate.
3. Jewelry with Gemstones:
- The GST rate for jewelry containing gemstones depends on the type of gemstone used.
-
Gemstones are generally classified into two categories:
- Precious gemstones, such as diamonds, rubies, emeralds, and sapphires, attract a 3% GST rate.
- Semi-precious gemstones, like amethyst, topaz, and garnet, also attract a 3% GST rate.
4. GST on Jewelry Manufacturing and Trading:
- Jewelry manufacturers are required to register under GST and charge the applicable GST rate on their sales. They can claim input tax credit on their purchases of raw materials and other inputs used in the manufacturing process.
- Jewelry traders also need to register under GST and charge the applicable GST rate on their sales. They can claim input tax credit on their purchases of jewelry from manufacturers or other traders.
Implications of GST on the Jewelry Industry
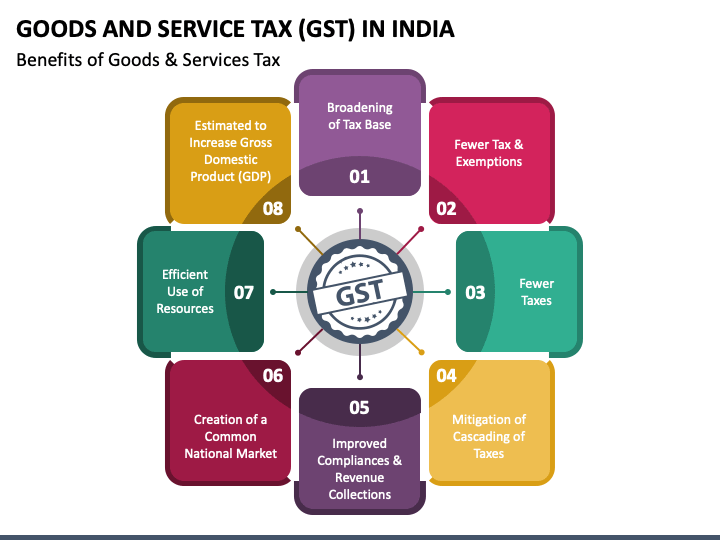
The implementation of GST has brought about significant changes in the jewelry industry, impacting both manufacturers and consumers. Some key implications include:
1. Simplified Tax Structure: The introduction of GST has simplified the tax structure for the jewelry industry, replacing a multitude of state-level taxes with a single nationwide tax. This has reduced compliance costs and administrative burdens for businesses.
2. Increased Transparency: GST has brought greater transparency to the jewelry sector, as all transactions are now recorded under a uniform system. This has helped to curb tax evasion and improve the overall tax collection efficiency.
3. Streamlined Supply Chain: GST has facilitated the seamless movement of goods across state borders, streamlining the supply chain and reducing logistical challenges.
4. Impact on Consumer Prices: The implementation of GST has led to a slight increase in the prices of jewelry for consumers. However, the overall impact on consumer prices has been minimal, as the GST rate for jewelry is relatively low compared to other goods and services.
5. Boost to the Unorganized Sector: GST has encouraged the formalization of the unorganized sector in the jewelry industry, as businesses are now required to register under GST. This has led to increased tax compliance and a more organized market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on GST for Jewelry
1. Is there any GST on gold coins and bars?
No, gold coins and bars are not subject to GST.
2. How is GST calculated on jewelry?
GST is calculated on the value of the jewelry, which includes the cost of the precious metal, gemstones, and any other materials used in its manufacture.
3. Who is responsible for paying GST on jewelry?
The ultimate responsibility for paying GST on jewelry lies with the final consumer. However, the GST is collected at each stage of the supply chain, with manufacturers and traders acting as intermediaries.
4. Can I claim input tax credit on GST paid on jewelry?
Yes, businesses registered under GST can claim input tax credit on GST paid on purchases of jewelry for use in their business operations.
5. What are the penalties for non-compliance with GST regulations?
Non-compliance with GST regulations can result in penalties, including fines, imprisonment, and cancellation of GST registration.
Tips for Navigating GST in the Jewelry Industry
1. Register under GST: All businesses involved in the manufacture, trade, or sale of jewelry must register under GST.
2. Maintain Accurate Records: Businesses need to maintain accurate records of all GST-related transactions, including invoices, receipts, and purchase orders.
3. Understand GST Rates: It is crucial to understand the applicable GST rates for different types of jewelry to ensure accurate invoicing and tax calculations.
4. Claim Input Tax Credit: Businesses should diligently claim input tax credit on GST paid on their purchases of raw materials and other inputs.
5. Stay Updated on GST Regulations: The GST regulations are subject to change, so businesses need to stay updated on the latest amendments and notifications.
Conclusion
GST has transformed the Indian jewelry industry, bringing about significant changes in taxation and compliance. Understanding the nuances of GST rates and regulations is essential for all stakeholders in the industry, from manufacturers and traders to consumers. By navigating the complexities of GST effectively, businesses can ensure compliance, minimize tax liabilities, and thrive in a competitive market.


%20in%20India%20explained.jpeg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Labyrinth: Understanding the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on Jewelry in India. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!